Reference : note values
The note value allows us to specify the duration of a sound. In the example below you can see the note values and their duration:
| Note | Name (USA) | Name (England) | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
Double Whole Note | Breve or brevis | Two whole notes |
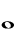 |
Whole Note | Semibreve | Two Half Notes or a half of a Double Whole Note |
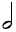 |
Half Note | Minim | Two Quarter Notes or a half of a Whole Note |
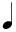 |
Quarter Note | Crotchet | Two Eighth Notes or a half of a Half Note |
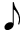 |
Eighth Note | Quaver | Two Sixteenth Notes or a half of a Quarter Note |
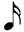 |
Sixteenth Note | Semiquaver | Two 32nd Notes or a half of an Eighth Note |
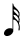 |
32nd Note | Demisemiquaver | Two 64th Notes or a half of a Sixteenth Note |
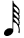 |
64th Note | Hemidemisemiquaver | Half of a 32nd Note |
| Names in other languages | |||
As you can see, each note is twice as long as the following note and half as long as the previous one.
NOTE: When we write eighths, sixteenths, thirtieths, and sixty-fourths, we usually group all notes within a "family" (note type) with a bar to make them easier to read:
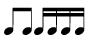
See Reading Music in the Tutorials section.
